NASA’s space probe
Voyager-1 has officially left the solar system, lead scientists have agreed.
The 2 Voyager spacecraft were launched in 1977, and made a «grand tour» of the outer planets in our solar system. They showed the world amazing close-up pictures of planets which until that moment had only been seen as vague blobs through a telescope. They also recorded vast amounts of scientific data on the planets, which increased our knowledge of them immensely. It’s fair to say that the Voyager program is probably the biggest success story of human space exploration.
In 1990, Voyager-1 was told to look back towards earth and take a picture. It became probably the most famous picture which consists almost entirely of blackness. If you look very closely, you can see a small blue pixel in there towards the right. That’s earth, the «pale blue dot» as Carl Sagan called it. If you want to feel small, this is the picture you should be looking at.
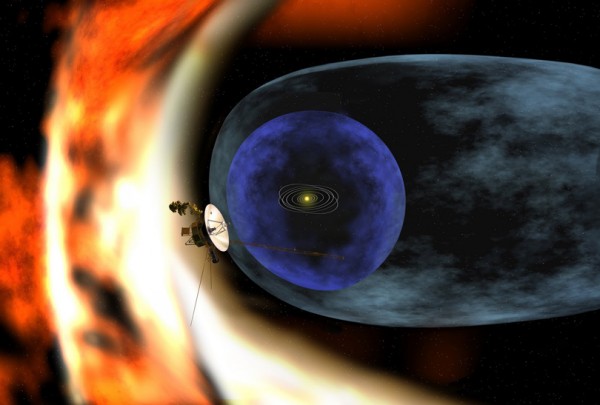
Now, 36 years after they were launched, the first of the Voyagers has left the solar system. Its twin brother Voyager-2 was actually launched first, but it took a different trip and is traveling at a lower speed. Voyager-1 is buzzing along at around 160,000 kilometers per hour. Even traveling at this speed however, it will not come near another star for the next 40,000 years. To cross our Milky Way galaxy at this speed would take 53 million years and the nearest neighbor galaxy is hardly worth thinking about. We expect power to run out in 10 years or so anyway, though in that time they can still teach us a great deal about the composition of the space they travel through.
![]()
It’s actually remarkable that they are still working at all. They had to survive multiple radiation spikes when flying close to the planets, and work at a temperature of −80°C. And in any case we are talking about 1970s technology. How many electrical things from 1977 do you have that still work today? Their signals are sent with a small low power transmitter, with only 23 watts of power. Even though the signal travels at the speed of light, it takes 17 hours to reach earth. This means that if the engineers at NASA send a signal to Voyager on a Monday morning, they will not receive a reply from the spacecraft until Tuesday evening.
It is difficult to understate the historic importance of Voyager-1 escaping our solar system. It is the farthest and fastest human made object in space, an almost eternal reminder of our existence which will travel the galaxy for, as near as makes no difference, forever. Long after our sun has died and taken our planet with it, the Voyagers will still be carrying images and sounds from earth on golden discs. Even if there is nobody out there who finds them, it is a nice thought nonetheless that this information will survive.
As far as we know, we might be the first life form in the history of the universe which manages to send something beyond its parent star system. This certainly deserves to be mentioned, and maybe even give ourselves a pat on the back. It makes one wonder, what we could do if we spent as much money on exploration as we currently spend on disagreeing with each other.
![]()